
An APP to assist with the differential diagnosis of patients with Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor
February 15, 2022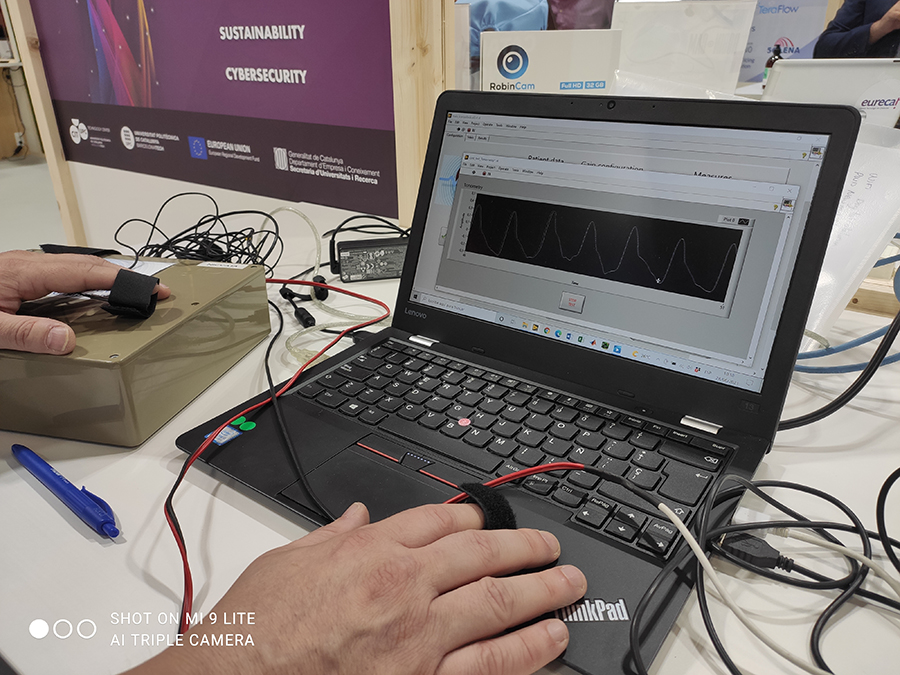
Cardiovascular Scale and other devices for fast, remotecardiovascular monitoring
February 25, 2022The Multimedia Applications Laboratory (LAM UPC) has developed an application that measures the anteroposterior movement of the tibia with respect to the femur to help in the diagnosis of anterior cruciate ligament knee injuries.
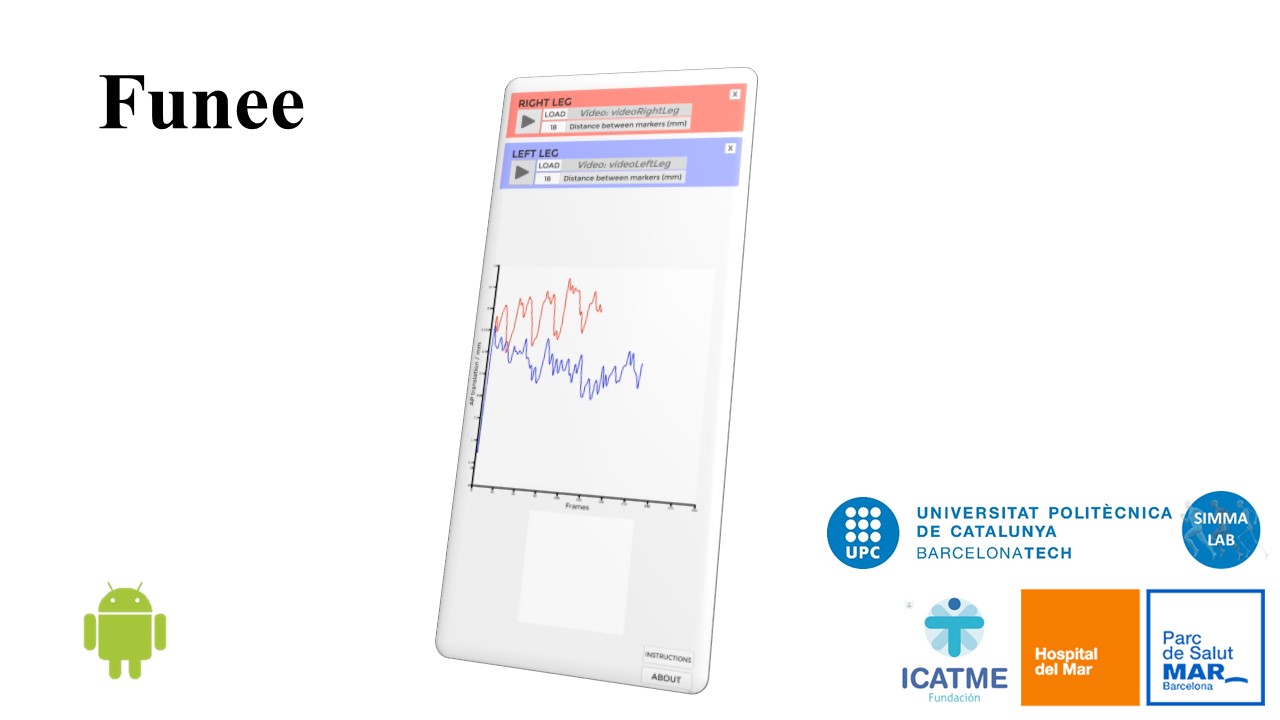
The process consists of two phases. First, surgeons record a 5–8 second video with their mobile phones while they carry out standard Lachman and Pivot-Shift tests on the injured area, on which three circular stickers have been placed. Then, once the video has been uploaded to the application, the movement between the tibia and the femur is calculated using image processing techniques (OpenCV library). In around ten seconds, the app can give a result that helps the doctor to form an objective diagnosis. A brief description can be seen in this video.

The application is available open on Android for Google Play at this link. It was developed jointly with the Catalan Institute of Traumatology and Sports Medicine (ICATME) of the Dexeus University Hospital and the Hospital del Mar in Barcelona. A viability test has been carried out in a sample of seven injured people and the results have been published in scientific journal.
Beyond the analysis of the injured person’s movement, work is being done on a project to develop an application that can predict the range of movement after a knee operation, using biomechanical optimisation and modelling. In the framework of this project, funding was obtained from the Ministry of Science and Innovation in the call “Europe Research 2020”.
Sector
You want to know more?
Related Projects
- A team from the Bioinspired Oral Biomaterials and Interfaces (BOBI) research group at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering (CEM) of the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya - BarcelonaTech (UPC) is taking part in the European project HYDROHEAL, which explores how to transform bone fracture treatment using smart and advanced biomaterials, aiming to reduce the risk of infection and implant rejection, as well as shortening fracture recovery times.
- Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's, and age-related disorders, have been widely studied due to their significant impact on individuals and society. So far, these are incurable and debilitating diseases that lead to progressive degeneration and death of nerve cells, resulting in cognitive and mobility impairments. Tremors, mainly at rest, slowness of movement (bradykinesia), limb rigidity, and issues with gait and balance are typical motor disorders related to Parkinson’s disease. Additionally, due to progressive muscle atrophy, these issues can lead to falls, which in turn result in further complications and risks to quality of life.
- The Biomaterials, Biomechanics, and Tissue Engineering (BBT) Research Group at the Institute for Health Research and Innovation (IRIS) of the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya – BarcelonaTech (UPC) is leading DYNAMIC, a project aimed at creating multifunctional, stimuli-responsive biomaterials that not only promote bone regeneration but also intelligently and effectively combat bacterial infections.
- 30/09/2024Project Headerrightno-repeat;left top;;auto20px A team from the Centre for Research in Biomedical Engineering (CREB) of the UPC and Sant Joan de Déu has created a new […]




