
GridForLoads: Stabilising the power grid through grid-forming loads
September 18, 2025
LIFE REMAR: Managed Aquifer Recharge for the Renaturalisation of Wastewater
September 25, 202522/09/2025
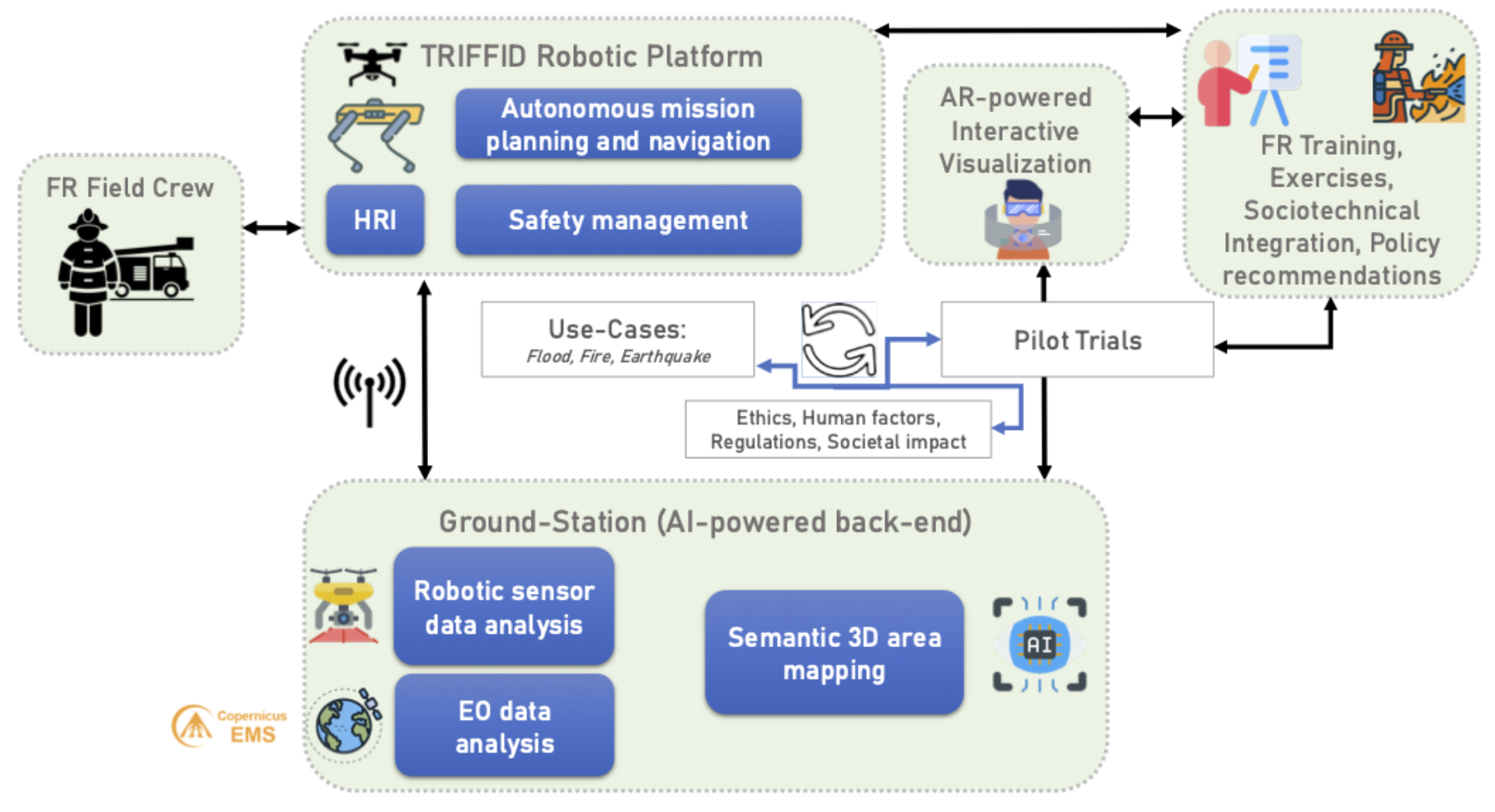
A research team led by the Mobile Robotics and Artificial Intelligence Group (RAIG) of the Institut de Robòtica i Informàtica Industrial (IRI, CSIC-UPC) at the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya - BarcelonaTech (UPC) is taking part in the European project TRIFFID (auTonomous Robotic aId For increasing FIrst responDers efficiency). The aim is to develop a platform to support rescue operations in emergency situations. The initiative combines advanced robotics, artificial intelligence and immersive interfaces to enhance safety and accelerate response in hazardous environments.
The TRIFFID project focuses on developing a system that combines the use of a ground and an aerial robot (UGV + UAV), capable of carrying out autonomous reconnaissance tasks powered by artificial intelligence (AI), thereby reducing the burden of human supervision. The data collected are displayed in real time on a control station equipped with an augmented reality interface, generating semantic maps of disaster scenarios and integrating them into European Civil Protection procedures.
In addition to its technological dimension, the project also addresses operational, legal and social aspects to ease the adoption of the solutions, and includes training tools for rescue personnel.
Impact
TRIFFID will help improve the efficiency of rescue teams, shorten response times and reduce human exposure to danger, with a significant decrease in planning and operational time, and an improvement in safety and decision-making in hazardous environments.
Consortium, budget and funding
The consortium consists of 12 partners from 9 European countries. Coordinated by HUA (Greece), and in addition to UPC (Spain), the project involves: HMU (Greece), VUB (Belgium), UWB (Czech Republic), CNR (Italy), DCNA (Austria), Telesto (Greece), ITML (Cyprus), PUI (France), GB (Netherlands), HFC and ROE (Greece).
The UPC, with the support of the IRI (CSIC-UPC), plays a key role in:
- Technical and scientific leadership: monitoring compliance with the project’s scientific and technological objectives throughout its duration.
- Leadership in robotic navigation and communications: developing advanced real-time methods for dynamic mission planning, autonomous navigation of ground and aerial robots, and safety management and recovery in the event of failures.
- Technical partner: designing and implementing the TRIFFID semantic mapping strategy, including LiDAR-based techniques, non-visual data analysis and information fusion.
TRIFFID has a total budget of € 4,098,690, fully funded by the European Union under the Horizon Europe programme (HORIZON-CL3-2023-DRS-01-05-101168042). The project will run for three years (October 2024 – September 2027).

Related Projects
- A research team from the inLab FIB at the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya - BarcelonaTech (UPC), together with the Asociación de Personas con Movilidad Reducida (AsoPMR), has taken part in the Spot4Dis project to enhance the mobility and autonomy of people with reduced mobility.
- The La Volta project foresees the construction of a large Catalan vault pergola within the Llars Mundet campus, in the Montbau neighbourhood (Horta-Guinardó district). This structure will become a new architectural landmark for Barcelona, combining traditional construction techniques with contemporary innovation. The project involves the Rehabilitation and Architectural Restoration Research Group (REARQ), at the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya - BarcelonaTech (UPC), and is led by the Architects’ Association of Catalonia (COAC) and the Barcelona Provincial Council.
SATE-VEG: A system for energy renovation of buildings that helps reduce the urban heat island effect
Researchers from the Architecture, Energy and Environment (AiEM) group at the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya - BarcelonaTech (UPC) have developed SATE-VEG, an external thermal insulation system with a vegetal coating that offers seasonally adaptive thermal behaviour, enhances urban biodiversity and promotes positive health effects. The system is made from organic materials, requires low maintenance and consumes minimal water.- A research team from the Interdisciplinary Group on Building Science and Technology (GICITED) at the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya – BarcelonaTech (UPC) is leading the BioSAFE project, which aims to develop sustainable building envelopes —mainly façades— designed according to sustainability, comfort and safety criteria, with particular attention to their acoustic behaviour and fire performance.




